Aeronautics
Aeronautics
Tunisia has become a growing hub for the aeronautics industry in North Africa, supported by its skilled labor force, proximity to Europe, and competitive production costs. The country has developed a solid reputation in the aeronautical value chain, specializing in engineering, maintenance, repair, and manufacturing. More than 80 companies operate in this sector, with a focus on producing aircraft components and providing services to major international clients such as Airbus, Boeing, and Safran. Tunisia’s primary advantage in the aeronautics sector is its human capital. The country boasts a highly educated workforce, with a strong emphasis on engineering and technical skills. Several institutions, such as the National School of Aviation Technicians (ENNA) and specialized aeronautical engineering programs, ensure a continuous supply of qualified professionals. Additionally, the Tunisian government’s investment incentives, including tax breaks and streamlined regulations, make it easier for foreign companies to establish operations in the country. Investors can capitalize on Tunisia’s robust aeronautics ecosystem by entering partnerships with local companies or establishing joint ventures. The country’s Free Trade Zones (FTZs) offer additional benefits, such as duty exemptions and customs facilitation. With Tunisia’s proximity to Europe, aeronautical components can be produced cost-effectively and quickly delivered to European clients. Given the global demand for aircraft components and maintenance services, Tunisia’s aeronautics industry presents a promising investment opportunity.
 Automotive Industry
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry in Tunisia is rapidly growing, particularly in the production of automotive components. The country has positioned itself as a major supplier of electrical and mechanical parts, wiring systems, and subassemblies for renowned car manufacturers such as Volkswagen, Peugeot, and Renault. Over 260 companies are active in the sector, employing more than 80,000 people and contributing significantly to the country’s export revenue.Tunisia’s automotive industry benefits from several competitive advantages. These include the country’s strategic geographical position, allowing easy access to European, Middle Eastern, and African markets. The sector also enjoys a well-established supply chain, with local manufacturers producing high-quality automotive parts at competitive costs. Additionally, the government’s pro-business policies, which include reduced corporate taxes, custom duty exemptions, and simplified export processes, are designed to attract foreign investors.As the global automotive industry shifts toward electric vehicles, there is potential for Indian companies specializing in EV technology to invest in Tunisia’s automotive sector, particularly in the production of batteries, motors, and charging infrastructure.Indian automotive firms can invest in Tunisia’s well-developed automotive component manufacturing sector, supplying European and North African markets. Tunisia’s strategic location and free trade agreements with the EU provide Indian firms with an opportunity to export automotive components with lower tariffs.
 ICT
ICT
Tunisia’s Information and Communications Technology (ICT) sector has experienced substantial growth and is a key contributor to the country’s economic development. The ICT industry in Tunisia is characterized by a vibrant ecosystem of startups, tech companies, and international corporations that specialize in software development, telecommunications, IT services, and business process outsourcing (BPO). The sector contributes approximately 7% of Tunisia’s GDP and employs over 80,000 people. Tunisia is recognized for its skilled IT workforce, boasting a large number of computer science graduates and engineers. The country ranks high in terms of innovation and technological adoption, supported by a strong internet infrastructure and a conducive business environment. Tunisia is also home to several tech hubs and incubators that provide support to startups and foster innovation. The government has implemented several initiatives to attract investment in the ICT sector, such as the creation of Technoparks and special tax incentives for tech companies. Tunisia presents numerous investment opportunities in the ICT sector, particularly in software development, cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and cybersecurity. Investors can tap into the growing demand for IT services, both locally and internationally. The BPO industry, which includes call centers and customer service operations, is another promising area for investment, as Tunisia’s multilingual workforce can serve clients across Europe and Africa. The country’s commitment to digital transformation and its growing reputation as a tech hub in Africa make ICT one of the most attractive sectors for investment.IT ecosystem. For example, the establishment of the India-Tunisia Centre for Innovation (ICT) in 2020 marks a critical step in enhancing technological collaboration between the two nations. This center aims to promote research, innovation, and the development of new technologies that can benefit both countries.
 Pharmaceutical Industry
Pharmaceutical Industry
Tunisia’s pharmaceutical industry is well-established, with a growing reputation for producing high-quality drugs and medical products. The sector comprises more than 40 pharmaceutical manufacturing companies, producing a wide range of products, including generics, over-the-counter medicines, and medical devices. The industry contributes significantly to Tunisia’s economy, supplying around 50% of the domestic market’s pharmaceutical needs and exporting to more than 30 countries. The pharmaceutical sector in Tunisia benefits from a skilled workforce, a strong regulatory framework, and state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities that comply with international standards. Tunisia’s strategic location also allows pharmaceutical companies to easily access European, Middle Eastern, and African markets. The government has introduced several initiatives to attract investment, including tax incentives, grants for research and development, and streamlined approval processes for new pharmaceutical products. Opportunities for investment in Tunisia’s pharmaceutical sector are abundant, especially in the areas of drug manufacturing, medical research, and biotechnology. Investors can establish production facilities, form partnerships with local companies, or invest in research and development to capitalize on the growing demand for pharmaceuticals in Africa and the Middle East. Tunisia’s focus on increasing local production of generics and biosimilars, along with its push for innovation in biotechnology, makes this sector ripe for investment. India is a significant exporter of pharmaceuticals to Tunisia, supplying affordable generic medicines and healthcare products. Tunisia imports a wide range of Indian pharmaceuticals, including essential drugs and medical devices. In recent years, India and Tunisia have discussed expanding their cooperation in the healthcare and pharmaceutical sectors. This includes exploring joint ventures for the manufacturing of pharmaceutical products in Tunisia, particularly in the production of generic medicines and biosimilars.
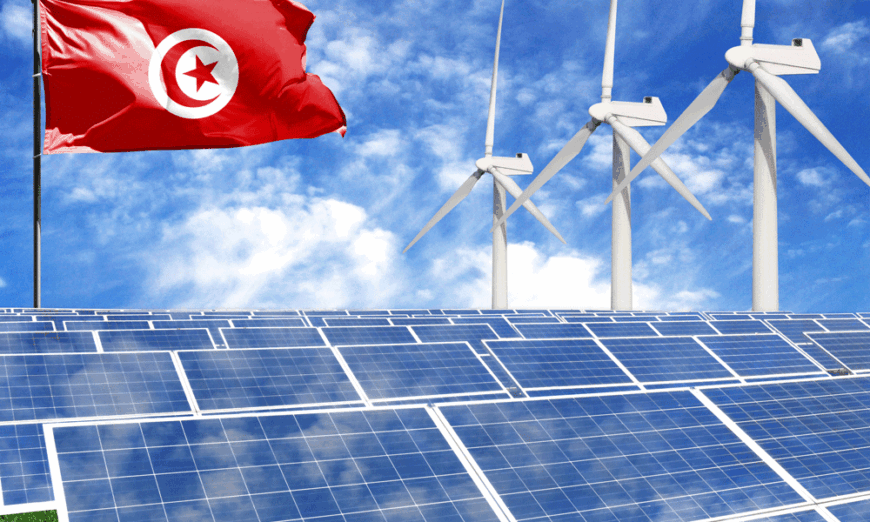
Renewable Energy
Tunisia is making significant strides in the development of renewable energy as part of its strategy to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and promote sustainability. The country’s renewable energy sector focuses primarily on solar and wind power, with ambitious plans to increase the share of renewables in the energy mix to 30% by 2030. Tunisia’s location offers an abundance of natural resources, including sunlight and wind, making it an ideal environment for renewable energy projects. The solar energy sector presents a particularly attractive investment opportunity, with several large-scale solar power projects under development. Tunisia’s desert regions provide optimal conditions for solar farms, and the government has implemented favorable policies to attract foreign investment in this area. Wind energy is another promising sector, with several wind farms already operational and plans to expand capacity in the coming years. The Tunisian government offers a range of incentives to encourage investment in renewable energy, including tax breaks, reduced tariffs, and grants for research and development. Additionally, Tunisia has signed several international agreements to promote green energy investment, providing investors with access to regional and global markets. There is also potential for investment in the development of renewable energy infrastructure, such as smart grids and energy storage systems. Tunisia is part of the ISA, an initiative led by India aimed at promoting the use of solar energy globally. This membership has paved the way for collaborative renewable energy projects, technology transfer, and joint investments in solar energy infrastructure.